Can Fintech development contribute to mitigating the greenhouse effect? A global perspective
Conference
65th ISI World Statistics Congress
Format: CPS Abstract - WSC 2025
Keywords: "ghg-emissions", fintech, greenhouse
Session: CPS 18 - Climate and Investment
Monday 6 October 5:10 p.m. - 6:10 p.m. (Europe/Amsterdam)
Abstract
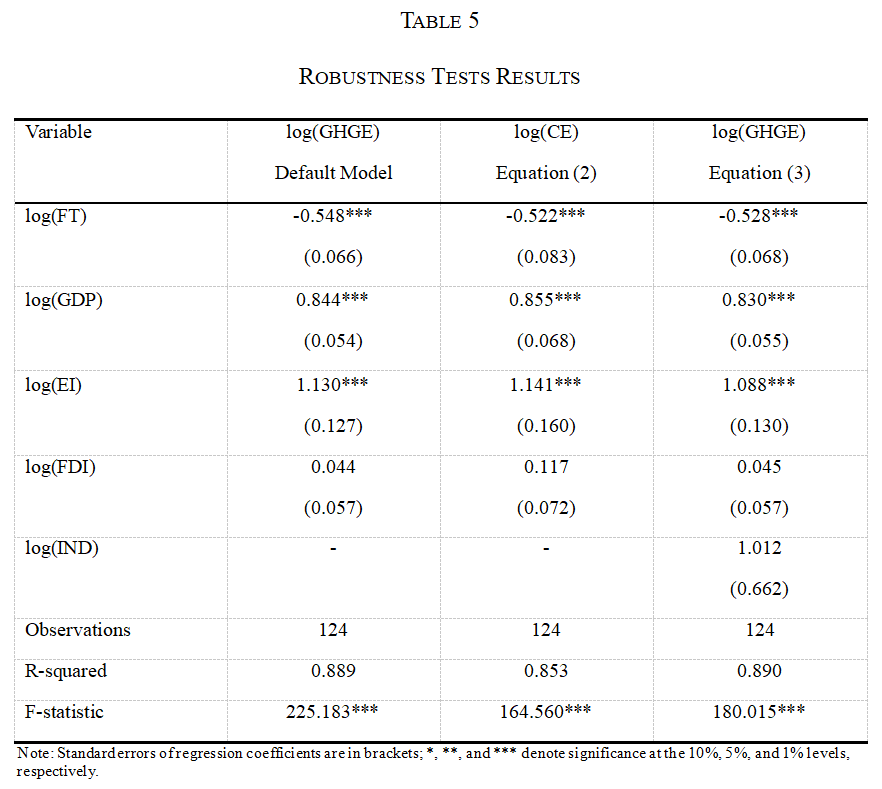
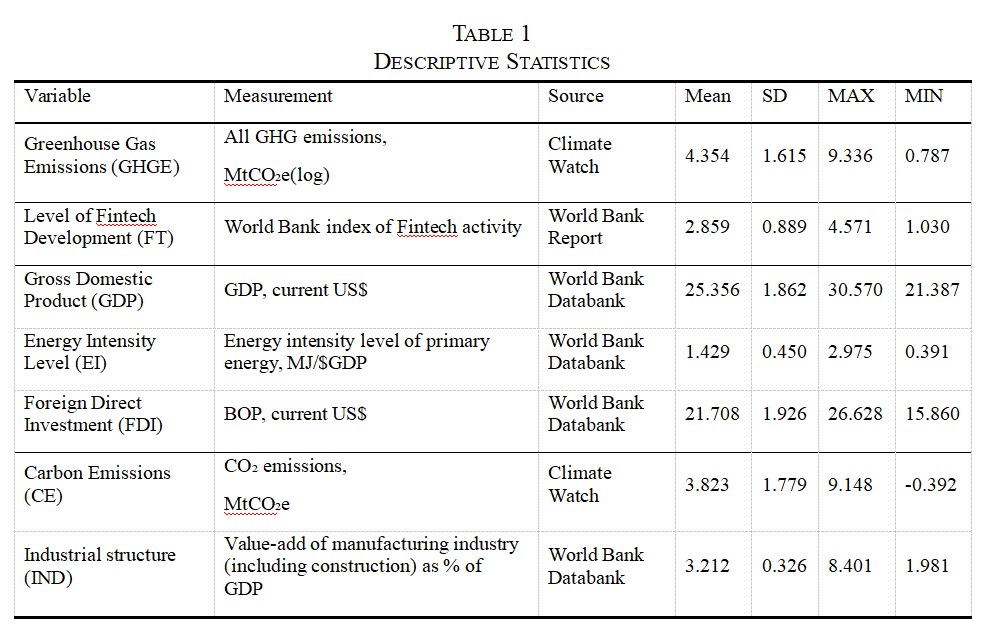
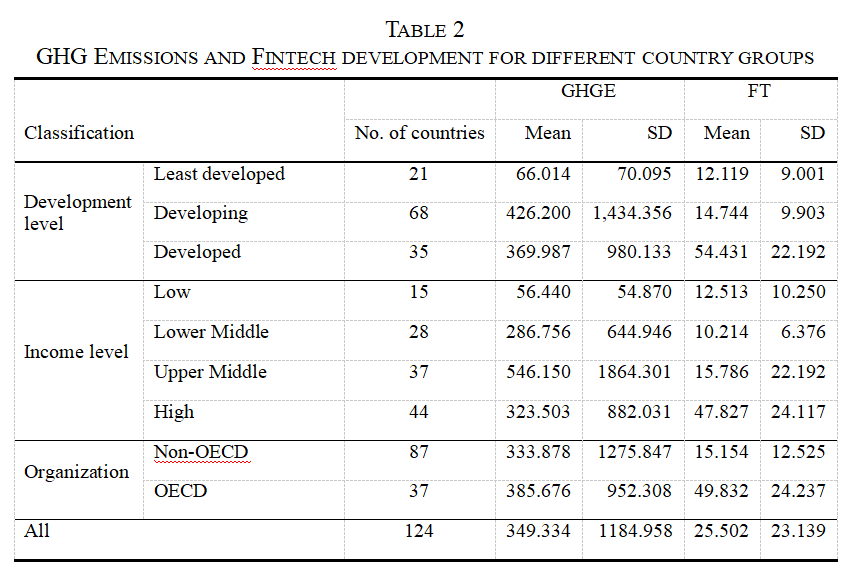
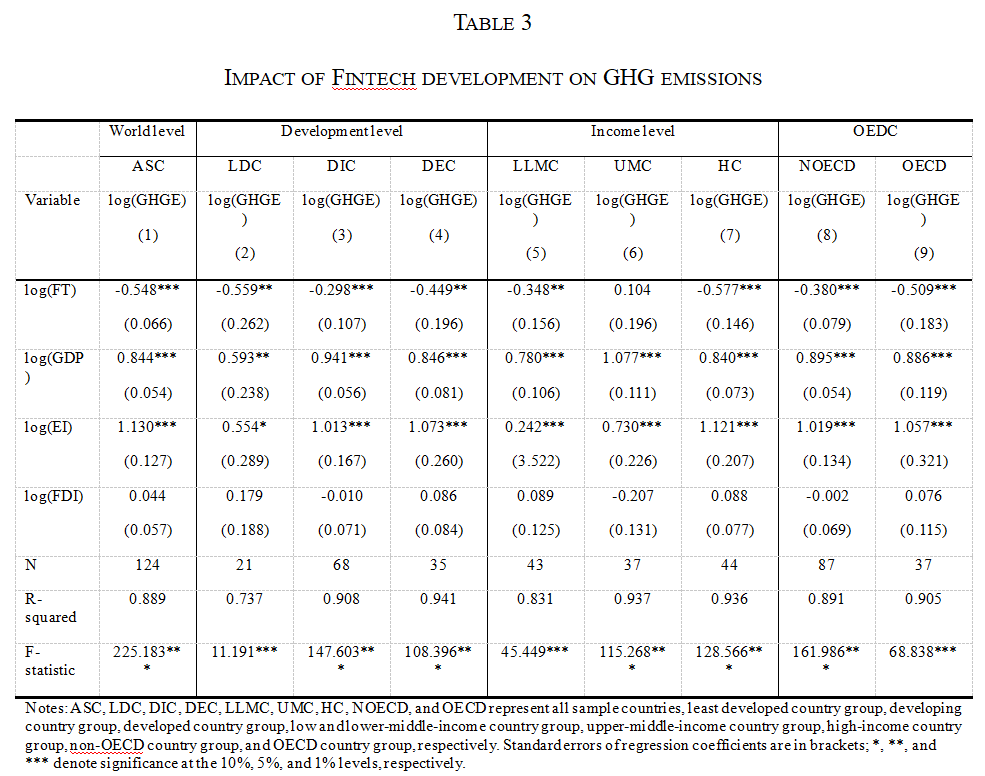
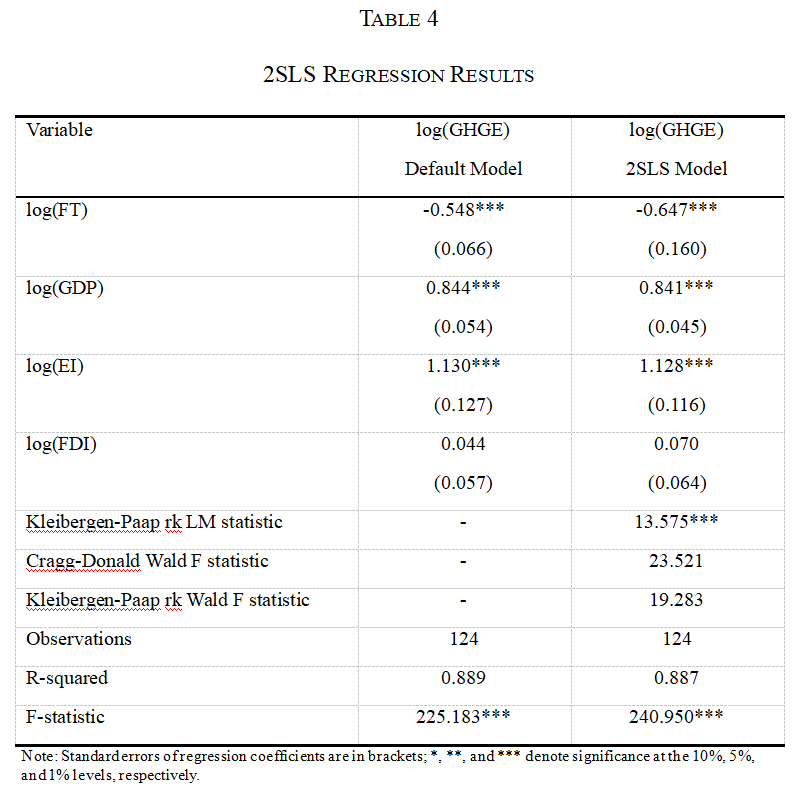
The integrated development of “finance” and “technology” has led to the rise of Fintech which uses technology to provide more efficient and inclusive alternatives to traditional finance. Additionally, by using blockchain technology and smart contracts Fintech allows for decentralized coordination of financial and economic activity. Increasingly Fintech is finding applications in green finance, supply chain transparency and other areas that could significantly impact greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This study analyzes the impact of Fintech development on greenhouse gas emissions from a global perspective. Using data from 124 countries from 2014 to 2018 and based on cross-sectional regressions, this study finds that, overall, Fintech development has a significant negative impact on greenhouse gas emissions. For every 1% increase in the Fintech development level, greenhouse gas emissions are reduced by 0.548%. Simultaneously, it examines the relationship between Fintech development and the greenhouse effect in different types of country groups in terms of the country’s development and income levels and membership in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The results show that the impact of greenhouse gas emission reduction of Fintech development is significant in low and high-income countries but not so for the upper-middle-income countries, supporting the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis. Several robustness checks are carried out, including using two-staged least-squares to test for endogeneity. The findings support policymakers in mitigating the greenhouse effect by promoting Fintech development.
Figures/Tables
1
2
3
4
5