Smartphone addiction and its implications among university students in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional survey
Conference
65th ISI World Statistics Congress
Format: CPS Abstract - WSC 2025
Keywords: smartphone
Session: CPS 8 - Statistical and Machine Learning Methods in Clinical and Public Health Research
Tuesday 7 October 4 p.m. - 5 p.m. (Europe/Amsterdam)
Abstract
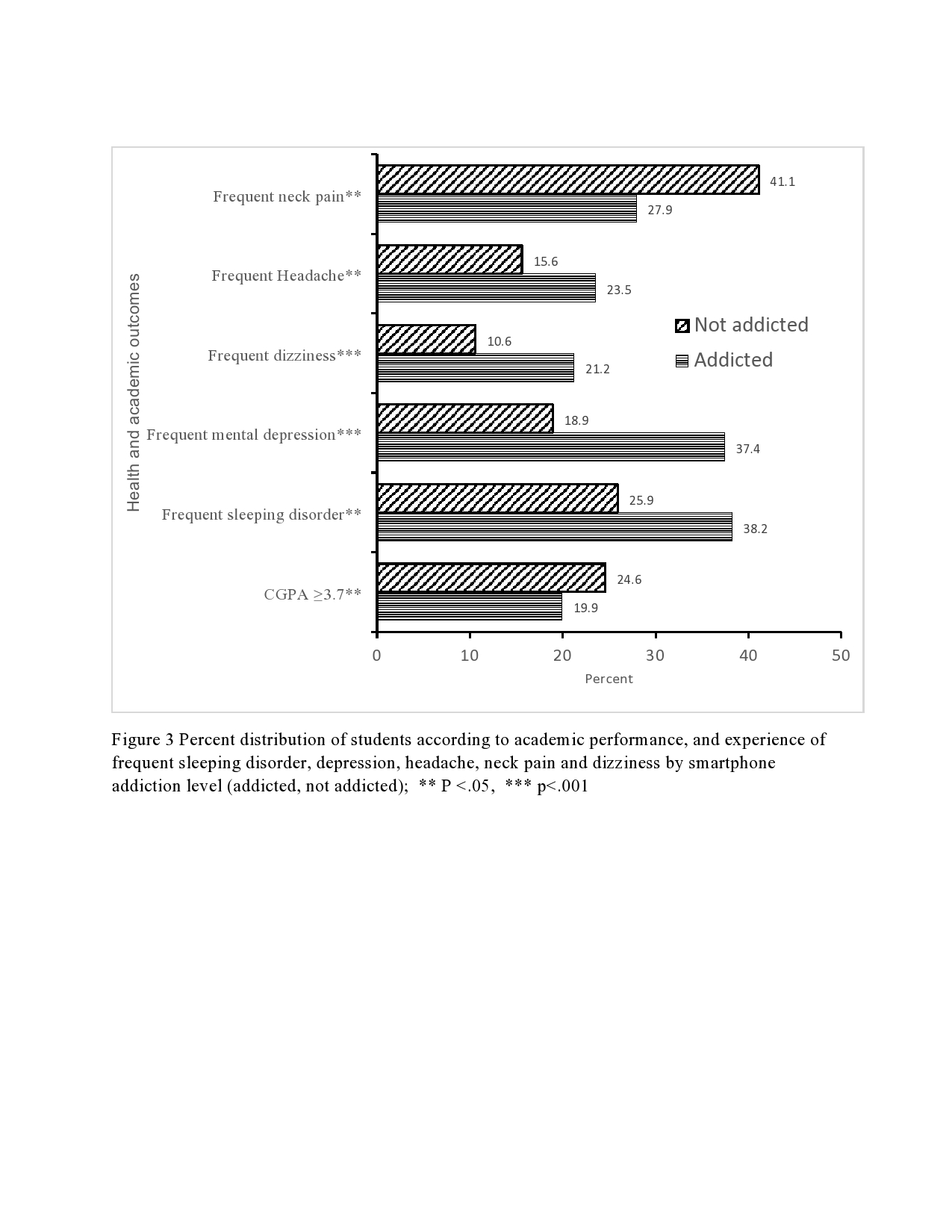
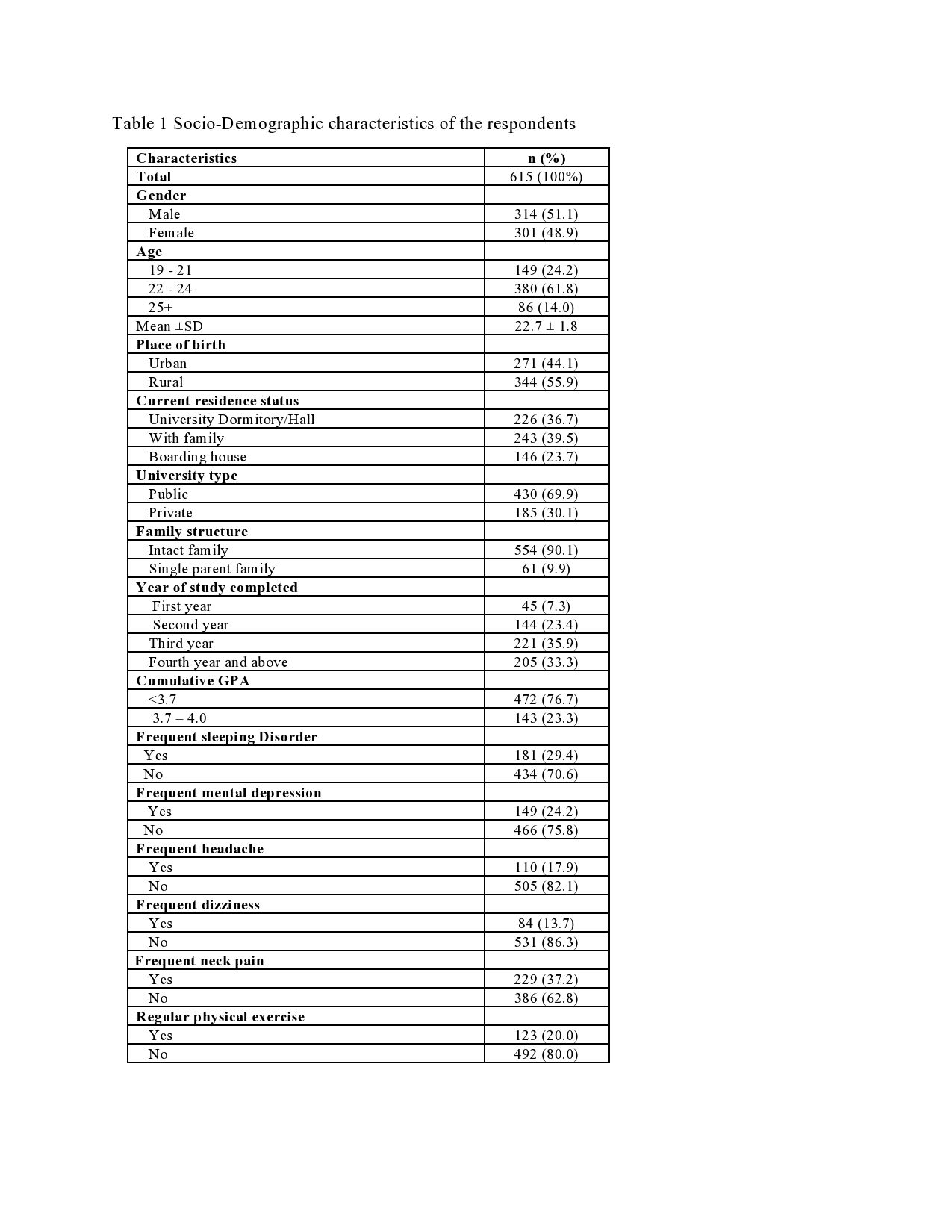
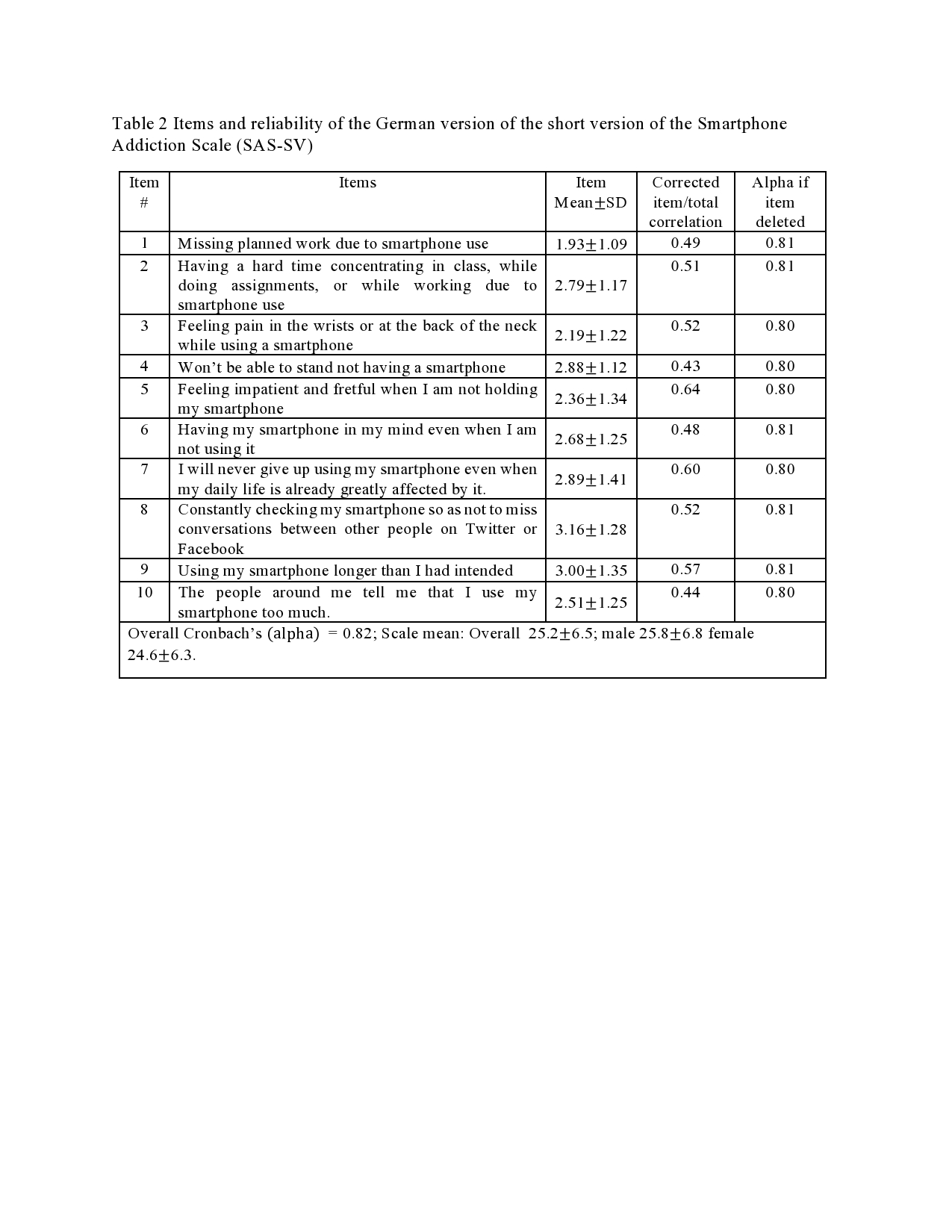
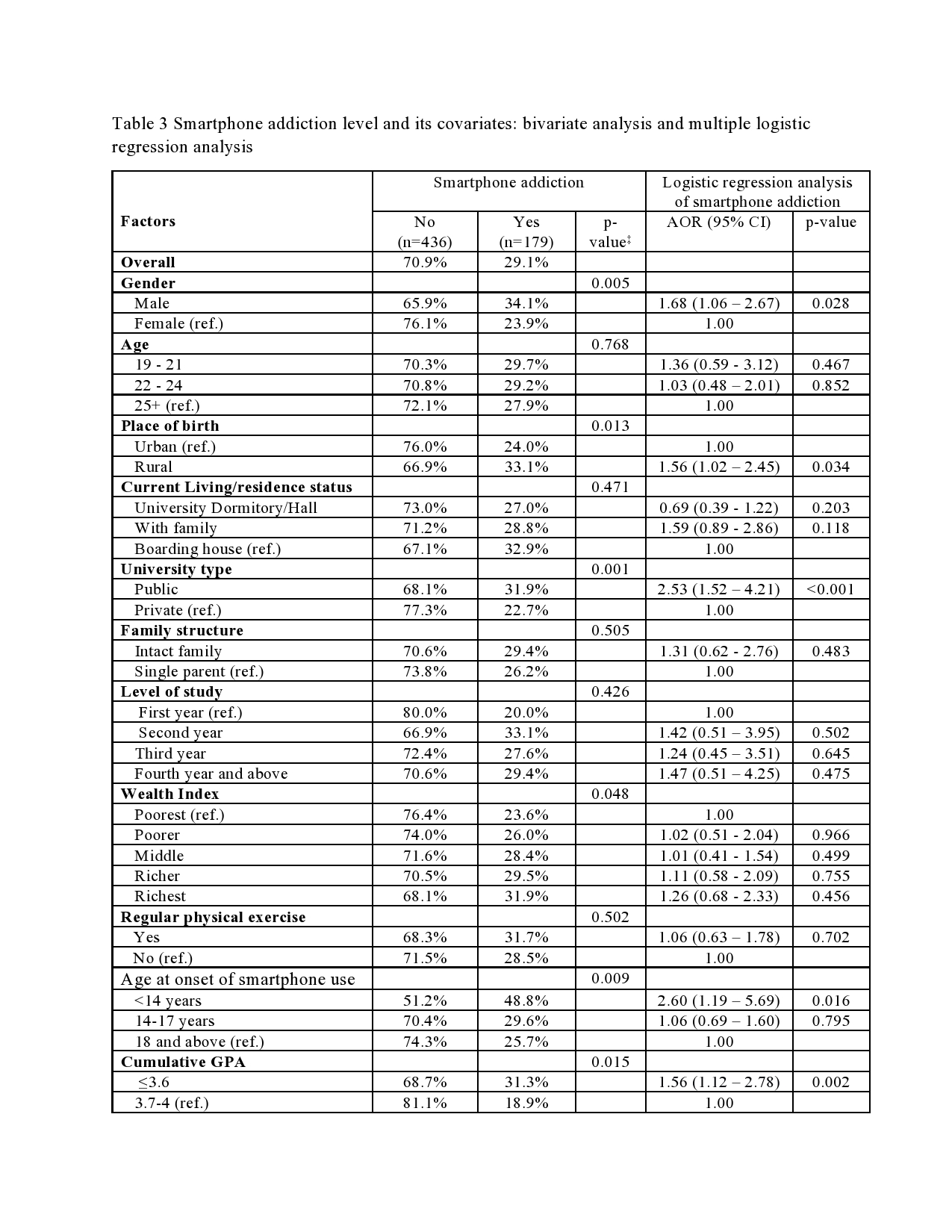
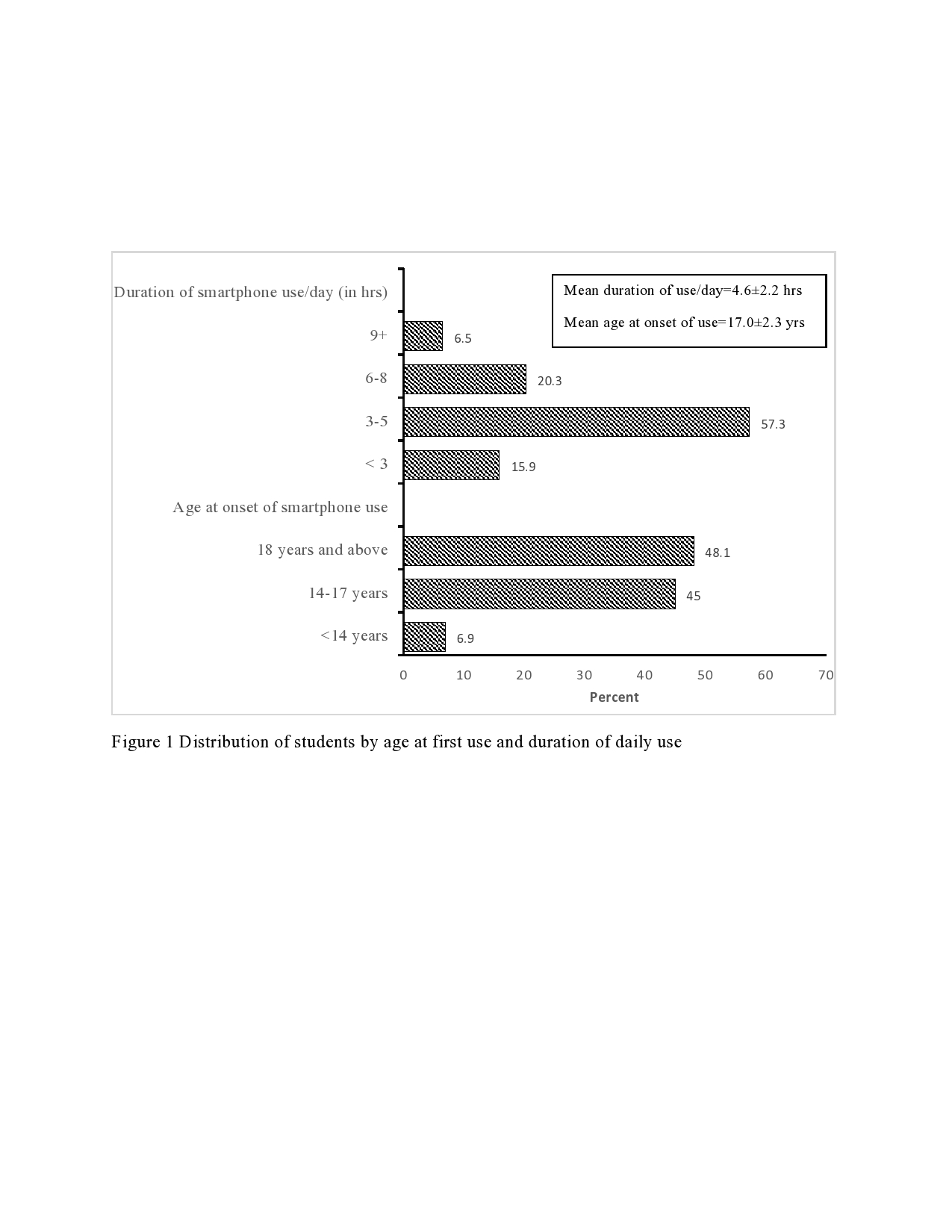
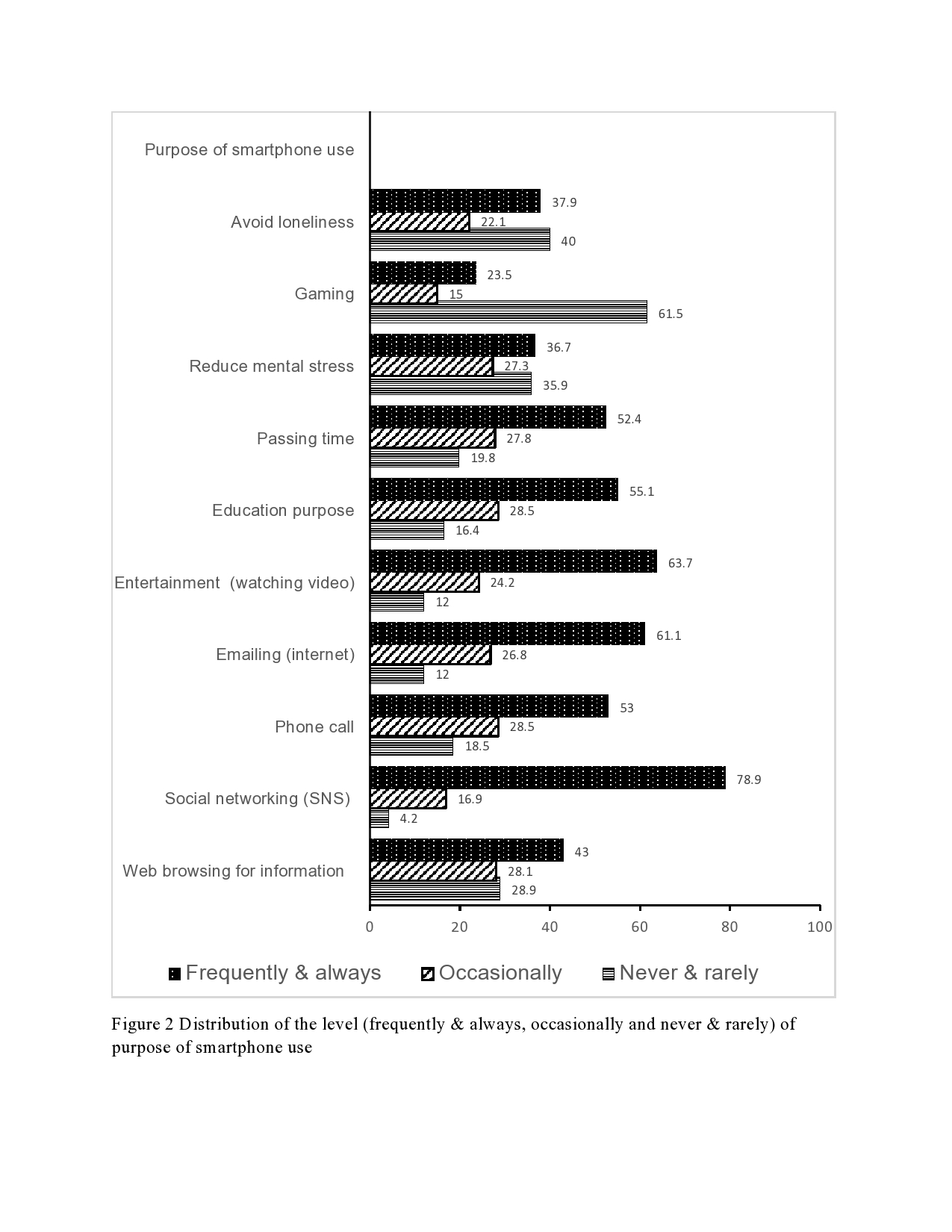
Introduction: Smartphones have become an essential and indispensable part of our daily life. Over the past decade, mobile phones have undergone tremendous technological transformation making them an attractive and must-have commodity for everyone, especially for the young population. Objectives: This study examined the smartphone use patterns, levels, and predictors of smartphone addiction (SA), and the impact of SA on students’ academic success, physical and mental health, and sleep disorder. Design: The study was based on a cross-sectional survey. SA was assessed using the short version of the “Smartphone Addiction Scale” (SAS-SV). Descriptive statistics and multiple logistic regression analysis were used for data analysis. Settings: Data were collected from students of both public and private sector universities in Bangladesh. Participants: Two-stage cluster sampling approach was used to derive 615 students from 7 (seven) universities in Bangladesh. Results: The results reveal that students spend on average about five hours daily on smartphones and they mostly use smartphones for social networking (79%), entertainment (64%), and emailing (61%). Overall 29% of students had an addiction to smartphones. A significantly higher risk of SA was observed among males, having a rural place of birth, students of a public university, low age at the onset of use of smartphones, longer duration of use of a smartphone, lower CGPA, and use of smartphone for the purpose of social networking, entertainment, gaming and passing time. Conclusions: This study suggests that SA may result in poor academic performance, physical as well as mental health problems, and sleeping disorders. There is a need for designing effective interventions including mass media campaigns and counseling to raise awareness about the risk of SA and its negative consequences on academic performance, health, and behavior of students.
Figures/Tables
page0001
page0002
page0003
page0006
page0007
page0008